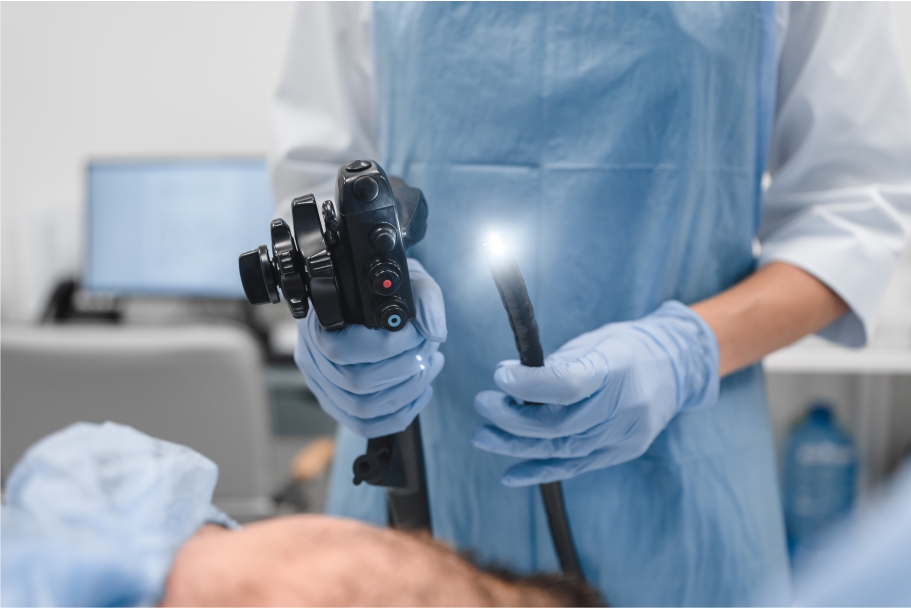
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that is used to examine organs inside the body. This process requires a flexible tube (endoscope) with a camera at the end. Endoscopy is performed to diagnose, treat and sometimes surgically intervene in diseases in many different parts of the body, especially in the digestive system.
Gastroenterologists often use endoscopy for early diagnosis of the stomach, esophagus, small intestine and large intestine. This process helps patients to diagnose their disease in a less invasive way.
How To Perform Endoscopy?
Endoscopy is usually performed in a hospital or clinic setting. Before the procedure, the patient is usually sedated, i.e. the patient is gently put to sleep or tranquilized with a relaxing medication. During an endoscopy, the patient lies on their back and the doctor inserts the endoscope into the body through the mouth or anus.
Since the endoscope contains a camera and a light source, the doctor can view detailed images of the organs on the screen of the device. In this way, stomach ulcers, reflux disease, inflammation, bleeding and other digestive problems can be easily detected.
Purposes of Endoscopy
Endoscopy is used to diagnose and sometimes treat various health problems. The main uses of endoscopy are as follows:
-
Diagnosis of Digestive System Diseases:
-
- Diseases in the organs of the digestive system such as the stomach, esophagus, small intestine and large intestine can be easily detected by endoscopy.
- Stomach ulcers, reflux disease, gastritis and other gastrointestinal problems can be detected at an early stage through endoscopic examination.
-
-
- Finding the source of bleeding:
- Bleeding in the stomach or intestines can be detected by endoscopy. Sometimes, the source of bleeding can be treated directly during endoscopy.
-
Biopsy Collection:
-
- During endoscopy, the doctor can collect biopsies from suspicious areas. This is an important step in the early diagnosis of serious diseases such as cancer.
-
-
Implementation of Treatment:
- Endoscopy may also include some treatment procedures. For example, narrowings in the esophagus can be widened, polyps can be removed or bleeding can be stopped.
Advantages of Endoscopy
Endoscopy allows digestive system problems to be diagnosed with less invasive methods. Compared to conventional surgery, it offers less pain, shorter recovery time and lower risk of complications. Moreover, endoscopy allows for a faster and more accurate diagnosis, which speeds up the treatment process.
Post Endoscopy Period
After endoscopy, the patient is usually kept under observation for a while. After the procedure, the patient may experience mild weakness or a sore throat (if endoscopy was performed through the mouth). These cases are usually short-lived and temporary. If a biopsy is collected, the results are usually available within a few days and your doctor will inform you about them.
Some patients may experience mild bloating or gas after endoscopy. This is also normal and usually disappears within a few hours.
When to Perform Endoscopy?
Endoscopy is usually recommended when there are abnormal findings, complaints or symptoms in the stomach, esophagus or intestines. Endoscopy is usually performed in the following cases:
- Persistent stomach pains, nausea or vomiting
- Swallowing difficulties or swallowing problems
- Unexpected weight loss or loss of appetite
- Bleeding or blood from the digestive tract
- Prolonged or severe heartburn (reflux)
When you have such complaints, your doctor may recommend that you have an endoscopy. Also, after certain ages or if there is a genetic predisposition, regular endoscopic checks may be recommended.
Endoscopy is an important medical procedure to maintain the health of the digestive tract and to detect possible diseases early. Endoscopic examination is usually painless and quick, but in some cases allows for more advanced treatment options. You can talk to your doctor for further information about endoscopy.
